Understanding Low Voltage Cabling Applications
Did you know that over 70% of today’s building systems rely on low voltage cabling to operate efficiently?
From the internet you use at home to the security systems in commercial buildings, these cables quietly power the essential technologies that keep our environments connected, secure, and automated.
Low voltage cabling refers to electrical wiring systems that carry voltages under 50 volts AC or up to 120 volts DC. These systems are designed for transmitting data, control signals, and small amounts of power. Because of their lower voltage, they offer a safer and more flexible alternative to traditional high-voltage wiring, making them ideal for a wide range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
In this article, we’ll explore the many ways low voltage cabling supports everyday technologies:
- What low voltage cabling is and how it works
- The different types of low voltage cables and their specific uses
- Applications in networking, security, audiovisual systems, automation, and more
- The key benefits of low voltage systems, including safety and cost-effectiveness
- Best practices for installation and long-term maintenance
By the end of this post, you’ll gain a clear understanding of how low voltage cabling applications help power the modern world, quietly, safely, and efficiently.
What Is Low Voltage Cabling?
Low voltage cabling refers to electrical wiring systems designed to carry currents at voltages below 50 volts AC or up to 120 volts DC. Unlike high-voltage systems that power large appliances and electrical outlets, low voltage cabling is used to transmit data, control signals, and small amounts of power to various devices and systems. This makes it a safer and more energy-efficient option for many modern applications.
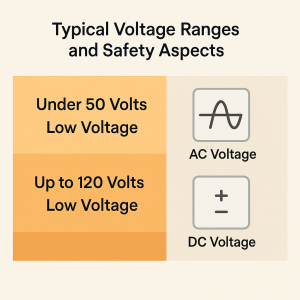
Typical Voltage Ranges and Safety Aspects
The low voltage classification is based on safety thresholds established to reduce the risk of electric shock and fire. In most cases, this includes:
- AC voltage under 50 volts
- DC voltage up to 120 volts
Because the voltage is lower, these systems are less likely to cause serious injury or ignite fires, making them ideal for environments where safety is a top priority. This also allows for easier installation and maintenance, often without the need for specialized high-voltage certifications.
Where Low Voltage Cabling Is Used
Low voltage systems are commonly found in a wide range of settings, including:
- Offices and commercial buildings: For networking, AV systems, and security.
- Factories and industrial facilities: Supporting automation and control systems.
- Homes: Powering internet, smart home devices, and entertainment systems.
- Schools and campuses: Facilitating communications, security, and classroom technology.
These environments rely on low voltage cabling to support critical infrastructure while maintaining safety and efficiency.
Types of Low Voltage Cables
Different applications require different types of low voltage cables. Each type is selected based on the specific needs of the system, such as speed, distance, and resistance to interference.
Twisted Pair Cables (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a)
These are the most commonly used cables in data networking. Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference. Key features include:
- Cat5e: Supports up to 1 Gbps speeds over 100 meters.
- Cat6: Handles up to 1 Gbps over longer distances and up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances.
- Cat6a: Supports 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter distance, ideal for high-performance networks.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables transmit data using light, providing incredibly fast speeds and long-distance capabilities with minimal signal loss. They are ideal for:
- High-speed internet backbones
- Long-distance data transmission
- Environments with high electromagnetic interference
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables are used for both data and video transmission and are common in:
- Cable television systems
- Security camera setups
- Certain AV systems
They offer strong shielding to minimize signal loss and interference.
Speaker and Thermostat Wires
These specialized cables are used in low-power applications like:
- Speaker wires: Deliver audio signals to speakers in home theaters and PA systems.
- Thermostat cables: Connect HVAC components like thermostats, sensors, and actuators.
Data Networking and Telecommunications
Low voltage cabling is the foundation of modern communication systems, enabling reliable and fast data transmission across networks.
Ethernet and Fiber for Internet and LAN
Cat6 and Cat6a Ethernet cables are essential for local area networks (LANs), offering:
- High-speed data transfer up to 10 Gbps
- Reliable connections for computers, servers, and network switches
- Compatibility with Power over Ethernet (PoE) to deliver power and data over a single cable
Fiber optic cables go even further, providing:
- Greater bandwidth and faster speeds than copper cables
- Long-distance transmission without signal degradation
- Resistance to electromagnetic interference
VoIP and Telephone Systems
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and traditional telephone systems both use low voltage cabling to facilitate communication. These setups benefit from:
- Lower installation costs
- Integration with digital networks
- Clear voice transmission with minimal interference
Low voltage cabling ensures that voice and data services can operate efficiently on shared infrastructure.
Security and Access Control Systems
Building security systems rely heavily on low voltage wiring to ensure continuous, reliable operation.
CCTV Cameras and Surveillance
Security cameras, whether analog or IP-based, use low voltage cabling for:
- Power supply via PoE or separate low voltage lines
- Video signal transmission to recording devices or cloud storage
- Integration with monitoring systems and mobile apps
Door Access and Alarm Systems
Access control and intrusion detection systems use low voltage wiring to connect:
- Card readers and keypads
- Electronic door strikes and magnetic locks
- Motion detectors and glass break sensors
- Alarm panels and sirens
These systems often operate on 12V or 24V DC, ensuring safe and efficient performance.
Building Automation and Smart Control
Modern buildings use automation systems to optimize energy use and improve occupant comfort, all supported by low voltage infrastructure.
HVAC, Lighting, and Occupancy Sensors
Low voltage cabling connects:
- Temperature sensors and thermostats
- Occupancy and daylight sensors
- Lighting controls and dimmers
- HVAC controllers and actuators
These systems communicate with a central building automation system (BAS) to adjust settings in real time, improving efficiency.
Protocols and Energy Efficiency
Standard control protocols supported by low voltage cabling include:
- 0-10V dimming: Allows smooth dimming of lighting fixtures.
- DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface): Enables advanced lighting control and monitoring.
These systems can reduce energy consumption by:
- 50–70% for lighting
- 20–30% for HVAC systems
Fire Alarm and Life Safety Systems

Low voltage systems are critical for safety in emergencies, especially in fire alarm and life safety applications.
NFPA 72 Compliance and Supervised Cabling
Fire alarm systems must comply with NFPA 72, which requires:
- Supervised circuits to detect cable faults
- Reliable operation during power loss (often with battery backup)
- Use of fire-resistant cable types
Emergency Alerts and Fail-Safe Operation
Low voltage cabling supports:
- Emergency call stations
- Mass notification systems
- Evacuation alarms and strobes
These systems are engineered to remain operational during outages, providing life-saving alerts.
Audiovisual and Communication Systems
AV systems in commercial, residential, and hospitality settings depend on low voltage wiring for seamless media delivery.
Office and Conference Room AV
Low voltage cabling connects:
- Projectors and digital displays
- Audio systems and microphones
- Video conferencing equipment
- Control panels and automation systems
Home Theaters and Intercoms
In residential settings, low voltage cabling supports:
- Surround sound systems
- Video distribution and streaming devices
- Intercom and doorbell systems
This allows for a fully integrated and immersive home entertainment experience.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Low voltage cabling plays a vital role in powering automation and smart technology across industrial and commercial spaces.
Industrial Ethernet and PLC Systems
Manufacturing and industrial environments use:
- Cat6a cabling for high-speed Ethernet connections
- 24VDC control wiring to connect sensors, actuators, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
These systems enable real-time control of machinery, robotics, and production lines.
Power Monitoring and Metering
Low voltage wiring transmits data from:
- Current transformers
- Voltage taps
- Energy meters
This information feeds into energy management systems for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Smart Homes and IoT Integration
Low voltage cabling is essential for integrating smart technologies in residential environments.
Lighting, Climate, and Security Integration
Smart home systems use low voltage cabling to:
- Control lighting scenes and schedules
- Automate climate settings based on occupancy
- Monitor and control security systems remotely
These features are typically managed through a central hub or mobile app.
Scalability for Future Technologies
Low voltage infrastructure is easily scalable, making it ideal for:
- Adding new smart devices
- Upgrading to faster internet or more secure systems
- Integrating with emerging technologies like AI-powered assistants and IoT sensors
This future-proofing ensures that homes and buildings remain adaptable.
Benefits of Low Voltage Cabling
Safety and Reduced Risk
Because it operates at lower voltages, low voltage cabling:
- Reduces the risk of electric shock
- Minimizes fire hazards
- Is safer to install and maintain
Cost and Installation Advantages
Low voltage systems are:
- Easier and faster to install
- Less expensive in terms of labor and materials
- Subject to fewer building code restrictions
Interference Reduction and Signal Quality
Low voltage cabling, particularly twisted pair and fiber optic, provides:
- Reduced electromagnetic interference
- Improved data integrity
- Clearer audio and video transmission
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Professional Installation Standards
Certified installers follow industry best practices, including:
- Selecting the right cable type for the application
- Avoiding signal interference from power lines
- Terminating cables correctly
- Testing and labeling all connections
Regular Inspection and Compliance
Ongoing maintenance includes:
- Periodic inspections for wear or damage
- Ensuring compliance with NFPA 72 and other codes
- Updating systems as technology evolves
The Foundation of Modern Connectivity
Low voltage cabling applications are central to the way we live, work, and communicate. From powering internet and phone systems to enabling smart home features, security, and automation, these systems are everywhere. Their safety, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make them indispensable in modern infrastructure.
Whether you’re planning a new installation or upgrading an existing system, understanding the capabilities and benefits of low voltage cabling is crucial. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, these systems offer a scalable and future-ready solution for homes, businesses, and industrial facilities alike.
